By Ginny Estupinian PhD, ABPP
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a widespread condition that develops after experiencing significant trauma. It can have severe repercussions for both personal life and relationships.
Treatment for PTSD is available and can help you feel better. However, individuals who have PTSD need to seek treatment as soon as possible.
Symptoms
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health issue that can develop after you have witnessed, experienced, or even directly participated in a traumatic event. These can include natural disasters, muggings, plane crashes, assaults, sudden deaths, and other life-threatening scenarios.
PTSD symptoms can range in intensity and are composed of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Therefore, regardless of severity, they can significantly impact all areas of your life – such as work or relationships.
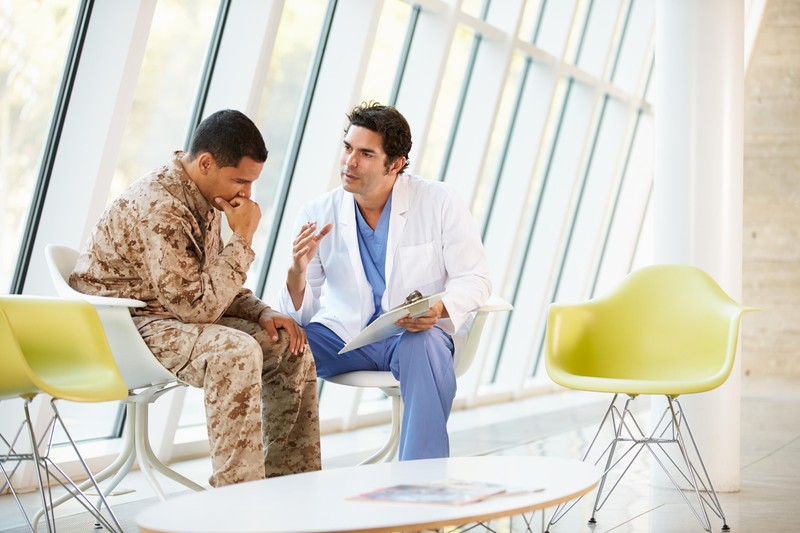
These symptoms may persist for months or longer and disrupt daily tasks like sleeping and eating. Speaking to a mental health professional is recommended if you experience any of these symptoms for over a month. They can assess your symptoms to determine if you have PTSD and suggest an effective course of treatment to aid in recovery.
People with Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) frequently experience unwanted and reoccurring memories, flashbacks, or nightmares. These memories can trigger strong emotions and physical reactions such as sweating, heart palpitations, or anxiety.
Avoidance is another common symptom associated with trauma. People may attempt to avoid places, people, or objects that trigger memories of the event. They may strongly react negatively to mundane things such as loud noises or accidents. These symptoms can impede someone’s daily activities and lead to difficulties in their social relationships. For instance, they may become isolated and distant from family, friends, or work. They may feel unable to express their emotions and develop the belief that they are untrustworthy or the world is unsafe. Additionally, they may lose interest in things they once enjoyed and exhibit behavior out of control.
Adults with PTSD may develop other mental health issues, such as depression or substance abuse, further complicating their situation. This condition is known as complex PTSD, and a combination of traumatic events and other elements like repeated exposure to violence or the sudden loss of family members causes it.
Causes
When a traumatic event happens to you or someone close to you, it’s normal to feel overwhelmed and distressed. Generally, though, after several weeks or months after experiencing the trauma, most people recover and move on with their lives.
PTSD is a disorder that may develop in some individuals after experiencing or witnessing an intensely traumatic event, such as death, injury, torture, or abuse. It could also arise from hearing about the traumatic incident experienced by someone close to them. Most people recover from PTSD without needing treatment. The primary symptom of PTSD is constantly feeling on edge and experiencing intense emotions such as nightmares, flashbacks, and anxiety. These sensations may cause you to avoid things or people that trigger memories of the traumatic event. Another common sign is feeling angry or guilty about what has transpired. This can make it difficult to think clearly or focus on the tasks at hand.
People may experience difficulty sleeping or remaining calm and serene. They may cling to a parent or other adult when feeling overwhelmed. It’s essential to remember that various methods are available for managing PTSD symptoms. A person with PTSD can take steps to lessen its impact on their life by learning active coping techniques and receiving support from family and friends.
Treatment
People who have Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can benefit from various treatments. Psychotherapy and medications, for instance, may reduce symptoms of PTSD while teaching people better coping mechanisms. Psychological techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy and exposure therapy are employed in PTSD therapy to help individuals alter negative thought patterns that may have emerged due to a traumatic event. Exposure therapy involves repeatedly subjecting yourself to trauma memory in a safe and controlled way. Examples include virtual reality programs, which have been known to be successful for veterans with PTSD, and EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing), which uses eye movements similar to those experienced during REM sleep.
Sometimes a combination of exposure and cognitive behavioral therapy is recommended. Research into PTSD continues to expand, and with it, new avenues of treatment will be developed. The hope is that one day soon, people exposed to trauma will not have to suffer long.